Nearly every new project requires approval—whether it's getting the green light from your team or securing support from executive stakeholders. While an informal email might suffice for smaller initiatives, significant business investments often require a well-crafted business case.
This guide, written by former consultants from McKinsey and Bain, will help you write a compelling business case. It provides the steps and best practices to secure the necessary support and resources for a successful project.
What is a business case
A business case is a written document (often a PowerPoint presentation) that articulates the value of a specific business project or investment. It presents the rationale for the project, including the benefits, costs, risks, and impact. The main objective is to persuade internal stakeholders to endorse the project.
A business case answers the questions:
- Why should we do this?
- What is the best solution?
- What will happen if we proceed with this investment decision?
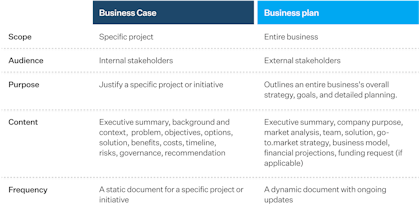
Business case vs. business plan
Simply put, a business case justifies a specific project or initiative, while a business plan outlines an entire business's overall strategy, goals, and detailed planning.
Investors use a business plan to make informed decisions about investing. It details the financial, strategic, and operational aspects of a business, helping investors assess the potential return on investment. In contrast, a business case is narrowly focused on a particular project or initiative. It helps stakeholders evaluate the potential impact of that specific project on the business. Both documents require thorough research, careful writing, and effective presentation.
Here's an overview of their differences:
Before writing your business case
The fate of your project or initiative will usually lie with a small group of decision makers. The best way to increase your chances of getting a green light is to engage with stakeholders, gather their insights, and build support before writing the business case. Use their input to construct a rough draft and present this draft back to key stakeholders for feedback and approval. Only once you have understood their priorities and concerns should you proceed with writing the final business case.
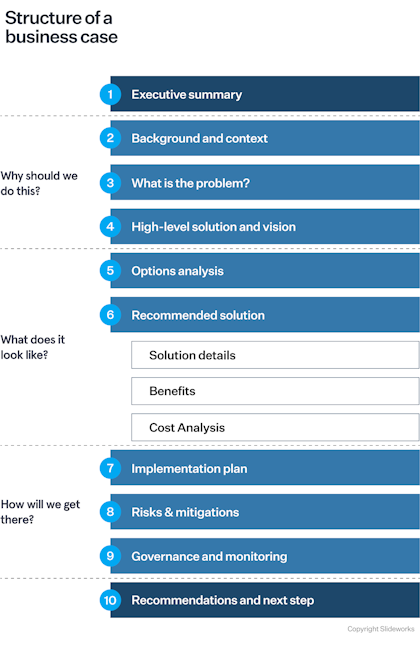
How to structure your business case
To get buy-in from your stakeholders, you must tell your "story" so that it is easy to understand the need, the solution you're proposing, and the benefits to the company. Generally, decision-makers will care most about ROI and how your project aligns with the organization's strategic goals – so keep those issues front and center.
In our experience, the business case structure below is the most logical and effective, but you should generally use whatever format or template your company uses. If no templates exist, use the structure below and find a solid template (you'll find a link to a template later in this post).
Whatever structure or template you apply, remember that your story needs to be clear above all else.
How to write a business case
Let's go through each of the 10 sections one-by-one:
1. Executive Summary
A one-page summary providing a concise overview of the business case.
Highlight the key points, including the problem or opportunity, proposed solution, and expected benefits.
We recommend structuring your summary using the Situation-Complication-Solution framework (See How to Write an Effective Executive Summary). The executive summary should be the final thing you write.
2. Background and context
Start with the why. Outline the situation and the business problem or opportunity your business case addresses. Clearly describe the problem's impact on the organization.
This section may include an overview of the macro environment and dynamics, key trends driving change, and potential threats or opportunities. Share data that conveys urgency.
For example: Is customer satisfaction dropping because of a lack of product features? Is an outdated IT system causing delays in the sales process? Are you seeing growing competition from digital-first players in the market? Are you seeing an opportunity as a result of changing customer needs?
3. What is the problem?
This is a key part of your business case. Your business case is built from your analysis of the problem. If your stakeholders don't understand and agree with your articulation of the problem, they'll take issue with everything else in your business case.
Describe the underlying issues and their solutions using data. You might include customer data, input from end users, or other information from those most affected by the problem.
4. High-level solution and vision
Start with a high-level description of the solution. Clarify the specific, measurable objectives that the project aims to achieve. Ensure these objectives align with the organization's strategic goals.
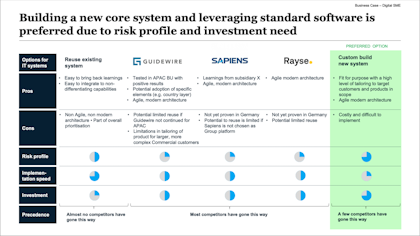
5. Option analysis
You have now answered the question: Why should we do this project? - and you have outlined a compelling solution.
In this section, you identify and evaluate different options for addressing the problem. Include a "do nothing" option as a baseline for comparison. Assess the pros and cons of each option, considering factors like cost, feasibility, risk, and potential benefits.
See a more in-depth article on how to think about and present risks in our blog post "Mastering Risk Mitigation Slides: A Best Practice Guide with Examples".
6. Recommended Solution
Solution Details
Propose the preferred solution based on the options analysis. Describe the solution in detail, including scope, deliverables, and key components. Justify why this solution is the best choice.
Benefits
Describe the benefits (e.g., cost savings, increased revenue, improved efficiency, competitive advantage). Include both tangible and intangible benefits, but focus on benefits you can quantify. Your stakeholders will want to know the financial impact.
Be very clear about where your numbers come from. Did you get them from colleagues in Marketing, Finance, HR, or Engineering? Stakeholders care about the sources for these assumptions and are more likely to trust your numbers if they come from (or are validated by) people they trust.
Cost Analysis
In this section, you provide a detailed breakdown of the costs associated with the proposed solution. Include initial investment, ongoing operational costs, and any potential financial risks.
Compare the costs against the expected benefits to demonstrate return on investment (ROI).
8. Risks and mitigations
In this section, you highlight potential risks and uncertainties associated with the project. Try to focus on the most important risks (you don't need to account for every potential scenario). These typically include those affecting cost, benefits, and schedule, but they can also include risks to the team, technology, scope, and performance.
Be realistic when you write this section. Transparency will gain the confidence of stakeholders and will demonstrate your foresight and capability.
Consider ranking your identified risk areas according to "likelihood of risk" and "impact of risk" (as shown in the example below). Then, propose mitigation strategies to manage and minimize risks.
9. Governance and monitoring
Establishing a clear governance structure ensures that there is a defined hierarchy of authority, responsibilities, and accountability. A definition of the following groups and roles are often included:
- Steering Committee: A group of senior executives or stakeholders who provide overall strategic direction, make high-level decisions, and ensure that the project aligns with organizational goals.
- Project Sponsor: An individual or group with the authority to provide resources, make critical decisions, and support the project at the highest level. The sponsor is often a senior executive.
- Project Manager: The person responsible for day-to-day management of the project, ensuring that the project stays on track, within budget, and meets its objectives. The project manager reports to the steering committee and project sponsor.
- Project Team: A group of individuals with various skills and expertise necessary to carry out project tasks. The team may include internal staff and external consultants.
You might also define what monitoring and reporting mechanisms that will be used to track the project's progress, identify issues early, and ensure accountability. These mechanisms often include specific Project Management Tools, ongoing status reports, and meetings.
10. Recommendations and next steps
In this last section, you summarize the key points of the business case and make a final recommendation to the decision-makers. Remember to Include your ROI number(s) again and repeat how your project aligns with the organization's strategic goals.
Consider ending your business case with a final slide outlining the immediate actions required to move forward with the recommended solution.
Business Case PowerPoint template
An effective business case requires both the right content and structure. A strong template and a few best practice examples can ensure the right structure and speed up the process of designing individual slides.
The Slideworks Business Case Template for PowerPoint follows the methodology presented in this post and includes 300 PowerPoint slides, 3 Excel models, and three full-length, real-life case examples created by ex-McKinsey & BCG consultants.
ROI calculator template
Often, companies have a preferred method of calculating a project's ROI. If this is not the case, you should use the one most appropriate to your project—break-even analysis, payback period, NPV, or IRR.
This free "Business Case ROI Template for Excel" can help you calculate project ROI and decide which method to use.
Download nowKey elements of a strong Business Case
Involve subject-matter experts
To develop a comprehensive business case, draw on insights from experts who understand the problem's intricacies and potential solutions. Involve colleagues from relevant departments such as R&D, sales, marketing, and finance to ensure all perspectives are considered.
Involve key stakeholders
Get input from all relevant team members, including HR, finance, sales, and IT. This collaborative approach ensures the business case is built on verified expert knowledge. Encouraging teamwork and buy-in from internal stakeholders helps build a strong foundation of support.
Understand audience objectives
Align your business case with the company’s strategic objectives and future plans. Clearly demonstrate how the project supports long-term company success. Consider the competition for resources and justify the investment by showing its relevance and importance.
Set a clear vision
Communicate the purpose, goals, methods, and people involved in the initiative clearly. Detail what the project aims to solve or achieve and its impact on the organization. This clarity helps stakeholders understand the overall vision and direction of the project.
Be on point
Be concise and provide only the necessary information needed for informed decision-making. Base your details on facts collected from team members and experts, avoiding assumptions. This precision ensures your business case is credible and actionable.
Frequently asked questions
What is the difference between a project business case and a project charter?
A project charter and a business case are distinct but complementary documents. The business case is created first and serves to justify the project's initiation by detailing its benefits, costs, risks, and alignment with organizational goals. It is used by decision-makers to approve or reject the project.
Once the project is approved, a project charter is often developed to formally authorize the project, outlining its objectives, scope, key stakeholders, and the project manager's authority. A summary of the business case is often included in the project charter.
How long should a business case be?
A comprehensive business case doesn't have a specific page count but should be detailed enough to clearly communicate the project's benefits, costs, risks, and alignment with organizational goals. For small projects, it may be a few pages; for larger or complex projects, it typically ranges from 10-20 word pages (30-50 slides), excluding appendices.
Sources: Harvard Business Press - Developing a Business Case